Cryptocurrency has had its ups and downs in news headlines and online forums. If you're considering investing in crypto, but feel unsure about how it works, learning about blockchain is a great starting point. Blockchain is the core technology behind Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies, with potential applications far beyond digital currency.
What is blockchain?
A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions in a continuous sequence, maintained across multiple computers (also called nodes) in a connected network. The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it difficult to hack or alter, providing a secure way for individuals to transact directly without intermediaries, such as banks or governments.
Originally developed to support Bitcoin, blockchain technology now powers various cryptocurrencies and has applications in property sales, medical records, legal contracts and more.
How blockchain works
Blockchain allows the recording and distribution of digital information without the ability to edit it. Here’s a basic breakdown of the process:
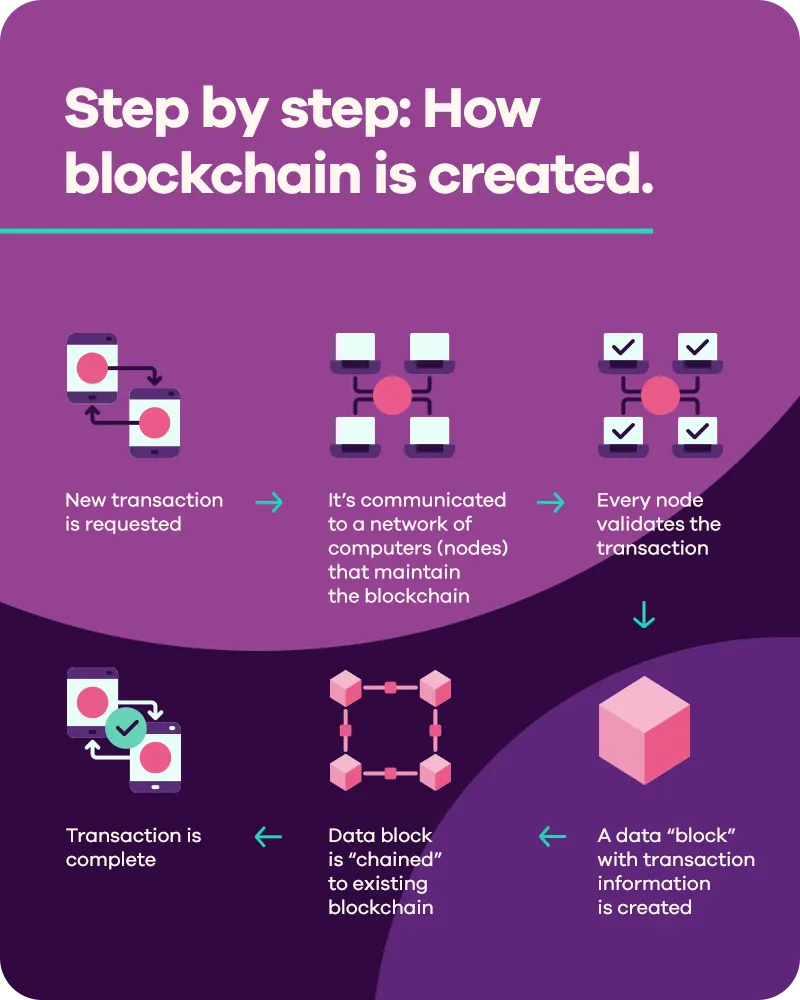
Blockchain vs. Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a type of digital currency, while blockchain is the ledger technology that records and tracks transactions. Although Bitcoin was the first application of blockchain, the technology has since found numerous other uses.
Key features of blockchain
Distributed ledger technology: All network participants have access to the shared ledger and its transaction history, which cannot be altered.
Unchangeable records: Transactions cannot be altered once recorded. Any error is corrected by adding a new transaction, both visible in the shared ledger.
Smart contracts: These are programs stored on a blockchain that execute automatically when predefined conditions are met.
Types of blockchains
Public blockchains: Open to everyone, allowing equal rights to view, send transactions and participate in verification. They are completely decentralized and primarily used for cryptocurrency exchange and mining.
Private blockchains: Controlled by a single organization, restricting access and participation. They are only partially decentralized.
Consortium blockchains: Governed by a group of organizations, these offer more decentralization and security than private blockchains.
Hybrid blockchains: These are controlled by a single organization with some level of public oversight for specific transaction validations.
Safety and risk
The more decentralized and widely distributed a blockchain is, the more secure it becomes. However, there are risks associated with cryptocurrency:
Hacking or losing your digital wallet: Digital wallets are susceptible to hacking and need strong security measures.
Volatility: Cryptocurrency values can be highly volatile and speculative.
Environmental concerns: Bitcoin mining consumes significant electricity, though some firms are exploring sustainable energy sources.
Advantages of blockchain
Decentralization: No single point of failure
Accuracy and security: Difficult to corrupt due to the need for network-wide validation
Traceability and transparency: Provides a trustworthy, chronological record of transactions
Growing applications
Blockchain technology is expanding beyond cryptocurrency. It is being used in healthcare for patient information, supply chain management for tracking shipments and estate planning for recording wills. This innovative digital ledger is poised to significantly impact various industries, changing how we live and work.


